
NIASWG
Namibian Invasive Alien Species Working Group (NIASWG)
About
The Namibian Invasive Alien Species Working Group (NIASWG) was established in 2022 as a collaborative effort between the Namibian government and non-governmental partners in response to the increasing threats caused by invasive alien plant species in Namibia.
Invasive alien plants and animals are one of the five major threats to global biodiversity and also cost global economies hundreds of billions of dollars each year. These are defined as non-indigenous species that adapt well to conditions where they are introduced and then spread or flourish rapidly, often in the absence of their natural enemies. If nothing is done to reduce the spread or eradicate these species, they can take over large pieces of agricultural and protected land, cause disease or injuries to both livestock and wildlife, negatively affect indigenous plants and animals, and ultimately damage native ecosystems.
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), under Goal 15 “Life on Land”, requires member states to, “by 2020, introduce measures to prevent and significantly reduce the impact of invasive alien species on land and water ecosystems and control or eradicate the priority species.” Namibia’s Second National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan 2013-2022 (NBSAP2), under Goal 8, directs that, “by 2018, priority measures are in place to control and manage the impact of invasive alien species in Namibia“.
Invasive alien species, both plants and animals, are of considerable concern in Namibia. They have a significant negative impact on indigenous biodiversity, agricultural production and sense of place. The numbers of invasive alien species in Namibia are increasing, as are population ranges and densities. Despite the introduction of alien species into local ecosystems requiring an Environmental Clearance Certificate under the Environmental Management Act of 2007, in practice there is little control and monitoring of alien species entering the country, being sold, distributed and propagated. The situation regarding invasive aliens is largely unregulated in Namibia. Recent actions to control and monitor invasive alien plants have been driven largely by civil society. Most of the work until now has focused on controlling plant species, since these are currently a bigger problem for Namibia than the animal species.
Winning the battle against invasive alien species requires a multi-pronged plan of action that involves the public, government, and non-governmental partners. The importance of addressing the growing problem of invasive alien species in Namibia and its increasing urgency prompted a group of ecologists and environmentally concerned individuals, from both government (central and local) and civil society to come together for a brainstorming meeting to discuss and debate the issue and to develop a prioritised Action Plan. The four main prongs of this Action Plan are:
- Prevent the import of potentially invasive alien species into Namibia;
- Stop the spread of existing invasive alien species within Namibia;
- Actively manage, control and, where possible, eliminate existing invasive alien species within Namibia;
- Establish an inclusive institutional mechanism to collectively implement the above Plan.
Visit the Action Plan tab to learn more.
Working Group documents
| NIASWG 5th Meeting 27 March 2025.pdf
Minutes of the 5th Meeting of the Namibian Invasive Alien Species Working Group 27 March 2025 at 14h15 |
|
| NIASWG 4th Meeting 24 Apr 2024.pdf
Minutes of the 4th Meeting of the Namibian Invasive Alien Species Working Group 24 April 2024 at 11h00 |
|
| NIASWG 3rd Meeting 6 December 2023.pdf
Minutes of the 3rd Meeting of the Namibian Invasive Alien Species Working Group 6 December 2023 at 10h00 |
|
| NIASWG 2nd Meeting 29 May 2023.pdf
Minutes of the 2nd Meeting of the Namibian Invasive Alien Species Working Group 29 May 2023 at 14h00 |
|
| NIASWG 1st Meeting 27 February 2023.pdf
Minutes of the 1st Meeting of the Namibian Invasive Alien Species Working Group 27 February 2023 at 09h00 |
NCWG Members
Chair:
Ministry of Environment, Forestry and Tourism, represented by Ms. Esmerialda Strauss, Deputy Director, Division: Forest & Botanical Research.
Deputy Chair:
Ms. Frances Chase, Head of Projects, Namibia Nature Foundation
Secretariat:
Secretariat services are currently provided by NCE: admin@n-c-e.org.
If you are interested in joining NIASWG please contact the Secretariat. Membership is free.
Member Organisations:

Association of Local Authorities in Namibia

Botanical Society of Namibia

City of Windhoek

Ministry of Agriculture, Water and Land Reform

Ministry of Education, Arts and Cultures

Ministry of Environment, Forestry and Tourism

Namibia Nature Foundation

Namibian Agronomic Board

Namibian Chamber of Environment

National Botanical Research Institute

NUST Biodiversity Research Centre
Action Plan
The NIASWG has drafted an Action Plan which has four main components:
- Prevent the import of potentially invasive alien species into Namibia;
- Stop the spread of existing invasive alien species within Namibia;
- Actively manage, control and, where possible, eliminate existing invasive alien species within Namibia;
- Establish an inclusive institutional mechanism to collectively implement the above Plan.
» Download the Action Plan to read more about the four components
Invasive alien species in Namibia
One of the tasks of the working group is to more clearly define which species are invasive aliens.
In Namibia, approximately 38 trees or large shrubs, 62 forbs and 24 grasses are considered invasive alien plants, 15 of which are serious economic and ecological threats. Many of the invasive shrubs are cactus species that flourish in Namibia’s arid environments, while aquatic weeds can choke the few permanent water sources in the country. Dry riverbeds and other disturbed areas are particularly vulnerable to invasion, which diminishes groundwater.
Several invasive alien animal species have been recorded in Namibia, including seven fishes, three reptiles, seven birds, four snails, one crayfish, two mussels and seven mammals. Eleven of these are considered serious threats to our native species. Besides outcompeting local species for space and resources (often the main threat), some invasive alien animals are similar enough to our native animals to interbreed with them and thus pose a genetic problem.
Plants |
|
Fish |
|
Reptiles |
|
Birds |
|
Snails |
|
Crayfish |
|
Mussels |
|
Mammals |
|
Resources
Namibia

Announcement of prohibition on importation of large predators and alien species of wild animals. 2019

Environmental Management Act. 2007

Environmental Management Act. 2007: Commencement, Activities and Regulations. 2012

Food for thought on AISWG. 2014

Import and Export Control Act 30 of 1994
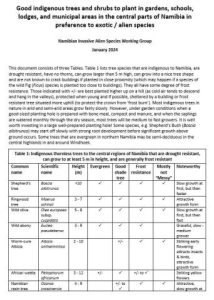
Indigenous trees and shrubs to plant in gardens, schools, lodges, and municipal areas in the central parts of Namibia. 2024

Invasive Alien Species Action Plan

Namibia's Second National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan 2013 – 2022

Namibia's Second National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan 2013 – 2022: Extracts

Proposed list of plants to be declared alien invasive in Namibia

Review of Legislation on Invasive Alien Species in Namibia including three Annexes. 2024

Sixth National Report to the Convention on Biological Diversity (2014-2018)
Abridged proceedings of the workshop on Alien Invasive Species in Namibia 2004. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Bethune S et al. 2004. National review of invasive alien species, Namibia. Consultancy Report on information collected regarding Invasive alien species in Namibia for the SABSP. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Boyer DC. 1989. Invasive alien plants in areas of the Namib Naukluft Park disturbed by man. Madoqua 16(2):137-139. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Brown CJ et al. 1985. Invasive alien organisms in South West Africa/Namibia. Brown CJ et al (Eds). South African National Scientific Programmes Report 119. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Government Gazette of the Republic of Namibia 2002. Government Notice, No. 231: Promulgation of Aquaculture Act, 2002 (Act No. 18 of 2002), of the Parliament. 1-22. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Government Gazette of the Republic of Namibia 2003. Government Notice, No. 91: Promulgation of Inland Fisheries Resources Act, 2003 (Act No. 1 of 2003), of the Parliament. 1-15. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Government Gazette of the Republic of Namibia 2003. Government Notice, No. 117 & 118: Commencement of the Inland Fisheries Resources Act, 2003 (Act No. 1 of 2003); Inland Fisheries Resources Regulations: Inland Fisheries Resources Act, 2003 (Act No. 1 of 2003). Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Government Gazette of the Republic of Namibia 2002. Government Notice, No. 245 & 246: Commencement of Aquaculture Act, 2002 (Act No. 18 of 2002), of the Parliament; Aquaculture (Licensing) Regulations: Aquaculture Act, 2002. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Government Gazette of the Republic of Namibia 2002. Government Notice, No. 71: Regulations relating to import and export of aquatic organisms and aquaculture products: Aquaculture Act, 2002. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Henschel JR & Parr T. 2009. Population changes of alien invasive plants in the lower Kuiseb River. Dinteria 31: 5-17. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Joubert DF. 2009. Invasive plants in Namibian subtropical and riparian woodlands. In: Kohli RK et al. (Eds). 2009. Invasive plants and forest ecosystems. CRC Press. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Klaassen ES & Kwembeya EG. 2013. A Checklist of Namibian Indigenous and Naturalised Plants. National Botanical Research Institute, Occasional Contributions 5. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Macdonald IAW & Nott TB. Invasive alien organisms in central SWA/Namibia: Results of a reconnaissance survey conducted in November 1984. Madoqua 15(1): 21-34. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Malan J. Discussion document on the regulation of alien and invasive species. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Ministry of Fisheries and Marine Resources (MFMR) 2001. Towards responsible development of aquaculture – Namibia’s Aquaculture Policy. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Schachtschneider K & February EC. 2013. Impact of Prosopis invasion on a keystone tree species in the Kalahari Desert. Plant Ecology 214(4): 597-605. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Shapaka TN et al. 2008. Invasive alien plants in the Daan Viljoen Game Park. Dinteria 30: 19-32. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Strohbach BJ et al. 2015. Prosopis encroachment along the Fish River at Gibeon, Namibia. I. Habitat preferences, population densities and the effect on the environment. Dinteria 35: 53-73. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Vinjevold RD et al. 1985. Invasive alien plants in the Namib-Naukluft Park. South African National Scientific Programmes Report 119: 24-27. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Williams D et al 2013. Impact of alien trees on mammal distributions along an ephemeral river in the Namib Desert. African Journal of Ecology 52(4): 404-413. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
International

Invasive Alien Species: A threat to biodiversity

IUCN Issues Brief: Invasive alien species and climate change

United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 15: Summary
Convention on Biological Diversity – Invasive Alien Species. Go to this link
Global Register of Introduced and Invasive Species (GRIIS). Go to this link
IUCN Global Invasive Species Database (GISD). Go to this link
Novoa A. et al. 2014. Introduced and invasive cactus species: a global review. AoB PLANTS 7. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Plaza PI et al. 2017. Rubbish dumps as invasive plant epicentres. Biol Invasions. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Stricker KB et al. 2015. Improving methods to evaluate the impacts of plant invasions: lessons from 40 years of research. AoB PLANTS 7. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Tsegay BT, Livingstone J and Fre Z (Eds) 2014. Exploring Prosopis management and policy options in the greater Horn of Africa. Proceedings of a regional conference. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
South Africa

Alien and invasive species regulations (South Africa)
Linking regulatory list to taxonomic backbone for Cactaceae

Presentation by Guy Preston to Namibia Scientific Society 29th May 2023

Presentation by Guy Preston to Namibian Invasive Alien Species Working Group 29th May 2023

Prioritisation of targets for weed biological control II

Prioritisation of targets for weed biological control III

South Africa’s National Listed Invasive Species – booklet

South African Alien and Invasive Species lists
An assessment of the information content of South African alien species databases. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya TA (Eds). 2020. Biological invasions in South Africa. Invading Nature – Springer Series in Invasion Ecology 14. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Holmes PM et al. 2005. A decision-making framework for restoring riparian zones degraded by invasive alien plants in South Africa: review article. South African Journal of Science 101: (11-12) 553-564. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Le Maitre DC et al. 2015. Impacts of invading alien plant species on water flows at stand and catchment scales. AoB PLANTS 7. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Shackleton RT et al. 2015. The impact of invasive alien Prosopis species (mesquite) on native plants in different environments in South Africa. South African Journal of Botany 97: 5-31. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Zachariades C et al. 2011. Biological control of mesquite (Prosopis species) (Fabaceae) in South Africa. African Entomology 19(1): 402–415. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Southern Africa
Bruton MN. 1985. Alien and translocated aquatic animals in Southern Africa: a general introduction, checklist and bibliography. South African National Scientific Programmes Report Number 113:1-72. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Macdonald IAW. 1994. Conservation implications of the invasion of southern Africa by alien organisms. PhD Thesis. University of Cape Town. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Peacock DS et al. 2007. The distribution and spread of the invasive alien common myna, Acridotheres tristis L. (Aves: Sturnidae), in southern Africa. South Africa Journal of Science 103: 465-473. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Stafford W et al. 2017. The economics of landscape restoration: benefits of controlling bush encroachment and invasive plant species in South Africa and Namibia. Ecosystem Services 27: 193–202. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
Walters M et al. 2011. Naturalised and invasive succulents of southern Africa. Samyn Y et al (Eds). 11:370. Download this resource from the EIS eLibrary
How can you help?
Help to support the identified actions . Get in touch if you need advice about invasive alien plants you might have on your property.
» Get involved with citizen science and record your sightings of alien plants
Record your sightings of carnivores on the Atlasing in Namibia website or the Atlasing in Namibia app.
Contact
Secretariat services are currently provided by NCE: admin@n-c-e.org.




